A Developer's Guide to SNOMED CT Code Lookup

If you've ever had to do a snomed ct code lookup, you probably know the pain of digging through massive database files or using clunky, slow web browsers. It's a process that can bring development and research to a grinding halt. But there's a much better way. Moving to an API-first approach makes the entire clinical vocabulary available on demand, with lookups taking less than 50 milliseconds.
This isn't just a minor improvement; it fundamentally changes how data engineers, researchers, and developers work with complex clinical terminologies.
Why Manual SNOMED CT Lookups Are a Thing of the Past
Not long ago, working with SNOMED CT meant downloading huge vocabulary files from places like OHDSI ATHENA, loading them into a local database, and then wrestling with complex SQL queries just to find a single code. The whole process was slow, error-prone, and a maintenance nightmare.
Your team was on the hook for everything: tracking new vocabulary releases, tuning database performance, and validating every data load. This old-school method created a bottleneck, forcing data scientists and developers to depend on database admins and infrastructure for every little thing. A simple lookup could easily balloon into a multi-day project bogged down by tickets and approvals.
The Shift to an API-First Strategy
An API-first strategy sidesteps all of that. Instead of wrangling a local database, your team can access SNOMED CT through a fast, secure REST API. The benefits are immediate and obvious.
- Zero Maintenance Overhead: Vocabulary updates are handled for you. You always get the latest version without any manual downloads or database migrations.
- Faster Development Cycles: With SDKs available for Python and R, developers can plug vocabulary lookups directly into their applications and scripts. You can find these on the OMOPHub Python SDK and OMOPHub R SDK pages.
- Incredible Performance: A well-built API with smart caching delivers query speeds that most local database setups just can't match.
We often see teams try to build and maintain their own vocabulary infrastructure, and it rarely ends well. The comparison below highlights why an API-first approach is the clear winner for modern development.
SNOMED CT Lookup Methods Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Database Approach | API-First Approach (OMOPHub) |
|---|---|---|
| Setup Time | Days to weeks | Minutes |
| Maintenance | Manual updates, patching, performance tuning | Fully managed, zero overhead |
| Performance | Variable; often slow without optimization | Consistently fast (<50ms) with caching |
| Accessibility | Limited to users with database access | Accessible from any application via REST API |
| Developer Experience | Requires complex SQL and data pipeline knowledge | Simple integration with Python/R SDKs |
| Scalability | Requires significant infrastructure investment | Scales automatically with demand |
Ultimately, the traditional model adds friction and slows down innovation, while the API-first model removes it.
This modern approach is what makes a vocabulary as massive as SNOMED CT truly usable. It's the most comprehensive clinical terminology in the world, with over 357,000 unique healthcare concepts organized into complex hierarchies. If you want a deeper dive, our guide explaining what SNOMED CT is is a great place to start. Its sheer scale is exactly why an efficient, modern lookup method is no longer a luxury—it's a necessity.
Executing Your First SNOMED CT Code Lookup
Jumping into your first snomed ct code lookup shouldn't feel like a chore. The quickest way to get a feel for the API is to hit the endpoint directly from your terminal. No code required, just a simple curl command.
Let’s try to find the concept for "Myocardial Infarction." This command pings the OMOPHub concepts endpoint, telling it to search for our term specifically within the SNOMED vocabulary.
curl "https://api.omophub.com/v1/concepts?query=Myocardial%20Infarction&vocabulary_id=SNOMED" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY"
Almost instantly, you’ll get a JSON response back. Look for the concept_id, concept_name, and domain_id. This is your instant gratification—it confirms your API key works and shows you exactly what the data structure looks like.
Integrating Lookups with Python and R SDKs
While curl is fantastic for a quick check, you'll eventually need to integrate these lookups into your actual data pipelines or applications. This is where the OMOPHub SDKs for Python and R really shine. They handle the boilerplate stuff like authentication and request formatting for you.
Tip: Before writing code, it's a good practice to test your query logic using a simple tool like
curlor Postman. This helps you confirm the endpoint and parameters are correct, saving debugging time later.
If you're working in Python, the code is remarkably straightforward. Once the library is installed, just instantiate the client with your API key and call the search_concepts function.
from omophub import OMOPHubClient
# Initialize the client with your API key
client = OMOPHubClient(api_key="YOUR_API_KEY")
# Search for "Myocardial Infarction" within SNOMED CT
concepts = client.search_concepts(
query="Myocardial Infarction",
vocabulary_id=["SNOMED"]
)
# Print the name and ID of the first result
if concepts:
first_concept = concepts[0]
print(f"Concept Name: {first_concept.concept_name}")
print(f"Concept ID: {first_concept.concept_id}")
For the R crowd, the experience is just as smooth. The R SDK follows a similar pattern, making the process feel familiar even if you switch between languages.
# Install the OMOPHub R SDK if you haven't already
# install.packages("omophub")
library(omophub)
# Set your API key
set_omophub_api_key("YOUR_API_KEY")
# Perform the SNOMED CT code lookup
concepts <- search_concepts(
query = "Myocardial Infarction",
vocabulary_id = "SNOMED"
)
# Display the first result
print(concepts[1, c("concept_name", "concept_id")])
As you're getting your feet wet, remember that tools like the ChatGPT Code Interpreter can be a huge help for generating or debugging small scripts like these. For more advanced use cases, the official documentation at docs.omophub.com has a wealth of detailed examples.
Exploring Concepts Visually: The No-Code Option
Sometimes you just want to poke around and explore the terminology without writing a single line of code. For that, the web-based Concept Lookup tool on the OMOPHub site is perfect. It's a great way to get a feel for the data before you commit to scripting. If you find yourself wanting more powerful visual tools, our guide on the SNOMED CT browser is a great next read.
The diagram below really captures the evolution from the old, clunky way of doing things to a modern, API-first approach.
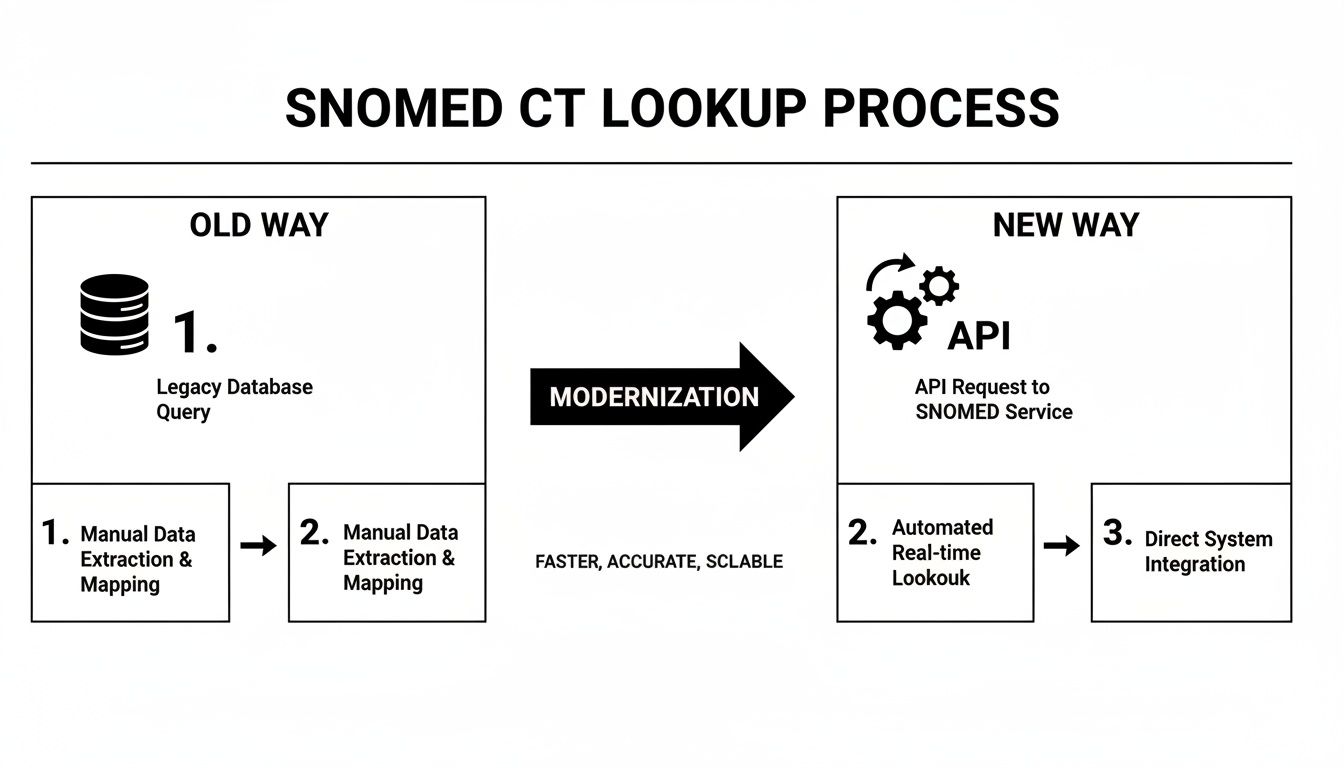
It’s a powerful illustration of how a well-designed API abstracts away all the backend database complexity. Instead of wrestling with direct queries and database maintenance, you get a clean, single point of entry that saves a tremendous amount of time and effort.
Navigating Concept Hierarchies and Relationships
A simple SNOMED CT code lookup for a single term is just the first step. The real power of SNOMED CT is its deep hierarchical structure, which lets you explore the relationships between different medical concepts. This is where things get interesting for real-world applications. Instead of just pulling one code, you can fetch entire sets of related codes—a crucial capability for building accurate patient cohorts or cleaning up messy source data.
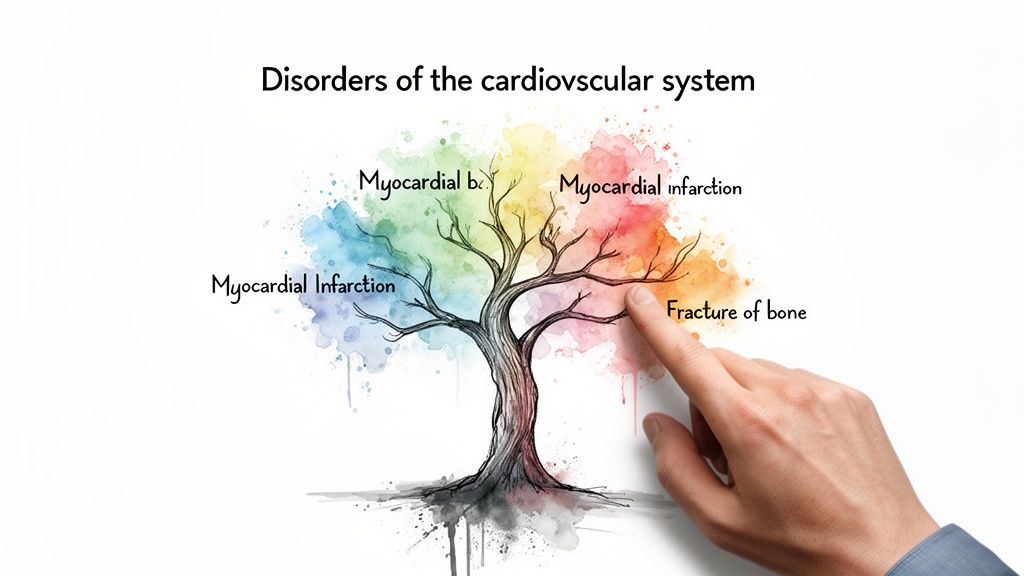
Think about a common research scenario: you need to find every patient with any kind of cardiovascular disorder. Trying to search for each specific condition by name would be a nightmare. With the hierarchy, you can start high up the tree with a broad concept like "Disorders of the cardiovascular system" and programmatically trace all of its descendants, from general conditions like hypertension down to very specific types of myocardial infarction.
Finding All Descendant Concepts
Let's walk through how this works in practice. We'll find all descendants of "Disorder of cardiovascular system" (SNOMED Concept ID: 106046006) using the OMOPHub Python SDK. The get_concept_descendants function handles all the heavy lifting for you.
from omophub import OMOPHubClient
# Initialize the client with your API key
client = OMOPHubClient(api_key="YOUR_API_KEY")
# Find all descendants for the cardiovascular disorder concept
descendants = client.get_concept_descendants(concept_id=106046006)
# Print the first few descendant concepts found
for concept in descendants[:5]:
print(f"ID: {concept.concept_id}, Name: {concept.concept_name}")
This single API call returns a full list of every related condition. It completely removes the need to write complex recursive SQL queries or maintain giant, static lookup tables. This kind of advanced SNOMED CT code lookup is exactly what makes robust cohort building possible.
This capability is a big reason why SNOMED CT's use in research has exploded. Between 2013 and 2020, its documented application in observational studies shot up from just 8 to 53, with cancer and drug research leading the charge. This growth highlights how the structured hierarchy allows researchers to pull precise patient data directly from EHRs and data warehouses. You can dig deeper into these trends in a detailed literature review on SNOMED CT usage.
Traversing Upstream to Parent Concepts
Navigating down the hierarchy is powerful, but sometimes you need to go the other way. You might have a very specific code from a source system, like "Fracture of shaft of femur," but for your analysis, you need to group it under a broader category like "Fracture of bone." This process of moving up the tree to find parent or ancestor concepts is a fundamental data standardization task.
Pro Tip: When you're standardizing data for the OMOP Common Data Model, mapping granular source codes to their standard parent concepts is a constant challenge. Using an API to find ancestors programmatically can dramatically simplify this crucial ETL step. For detailed parameters, check the official OMOPHub documentation.
The R SDK from OMOPHub offers an equally simple way to find these ancestors. The example below shows how to find the parent concepts for "Myocardial infarction" (Concept ID: 4329846).
library(omophub)
# Set your API key
set_omophub_api_key("YOUR_API_KEY")
# Find the ancestors of "Myocardial infarction"
ancestors <- get_concept_ancestors(concept_id = 4329846)
# Print the resulting ancestor concepts
print(ancestors)
This is the kind of functionality that becomes indispensable in data standardization pipelines, making sure that different source terms are all mapped consistently into the OMOP CDM. For more examples and detailed function parameters, the official OMOPHub API documentation is the best place to look.
Mapping SNOMED CT to Other Standard Vocabularies
A SNOMED CT code lookup rarely happens in a vacuum. Let's be honest: real-world clinical data is a tangled mess of different terminologies. A diagnosis might live in the EHR as a SNOMED CT concept, but the billing department needs it in ICD-10-CM. Lab results? They’re probably coded in LOINC. And prescriptions are almost always in RxNorm.
Connecting these disparate vocabularies is one of the biggest headaches in any data integration or ETL pipeline. It’s where the real work begins.
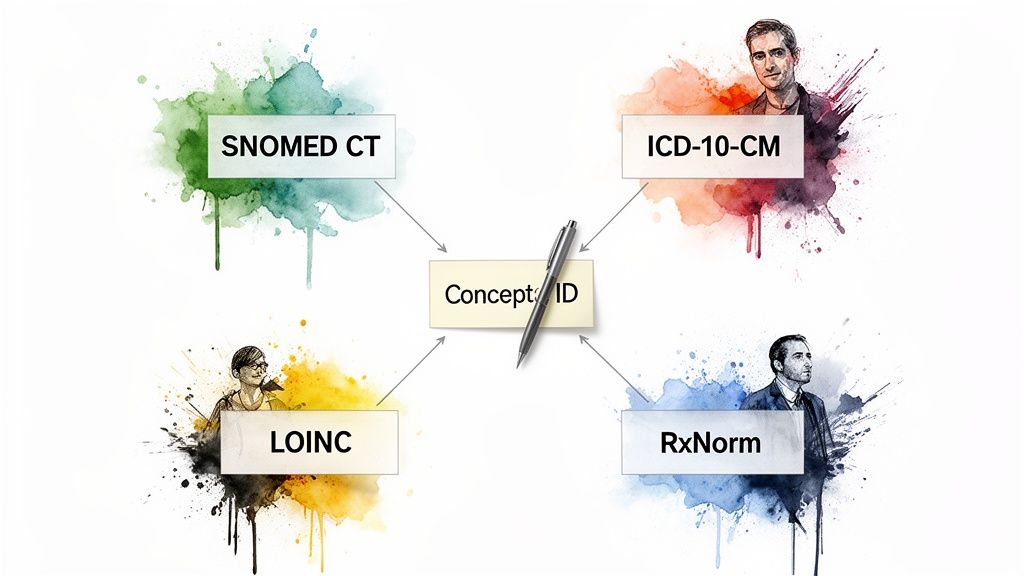
This is precisely why programmatic mapping is so critical. The entire goal is to take a concept from one system and reliably find its equivalent in another. Thankfully, we can lean on the carefully curated relationships within the OHDSI ATHENA vocabularies to do the heavy lifting. A classic example is taking a SNOMED CT concept for a diagnosis and programmatically finding its corresponding ICD-10-CM billing code.
A Practical Example: Mapping a Diagnosis for Billing
Think about a routine workflow. A patient is diagnosed with "Essential hypertension," which the clinician records in the EHR using the SNOMED CT code 59621000. To get paid, the billing system needs the right ICD-10-CM code. The OMOPHub Python SDK makes this translation a simple, direct operation.
The trick is to ask for related concepts but filter down to the specific relationship that matters. In this case, the relationship ID 'Maps to' is our golden ticket—it explicitly links the source concept to its intended target.
from omophub import OMOPHubClient
# Initialize the client with your API key
client = OMOPHubClient(api_key="YOUR_API_KEY")
# Find concepts related to "Essential hypertension" (SNOMED ID: 59621000)
# and filter for ICD-10-CM mappings.
related_concepts = client.get_related_concepts(
concept_id=59621000,
relationship_id=["Maps to"],
vocabulary_id=["ICD10CM"]
)
# Print the mapped ICD-10-CM code
if related_concepts:
icd10cm_mapping = related_concepts[0]
print(f"SNOMED CT Name: Essential hypertension")
print(f"Mapped ICD-10-CM Code: {icd10cm_mapping.concept_code}")
print(f"Mapped ICD-10-CM Name: {icd10cm_mapping.concept_name}")
This little piece of code automates what would otherwise be a soul-crushing manual lookup, dramatically improving accuracy and saving a ton of developer time. It's a perfect demonstration of how an API-first approach can smooth out critical operational workflows. This is the foundation of high-quality data standardization, a topic we explore more deeply in our article on semantic mapping.
Pro Tip: Always specify the
relationship_id(like 'Maps to') when doing a cross-vocabulary SNOMED CT code lookup. This ensures you get the official, curated mapping, not just a broad, associative link. For anyone building ETL pipelines for the OMOP CDM, getting this right is non-negotiable.
When you handle these mappings programmatically, you're building resilient, accurate data pipelines. You’re systematically turning that messy, multi-vocabulary source data into the clean, standardized format that’s actually useful for analytics and research. For more examples like this, dive into the official OMOPHub documentation.
Optimizing for Performance and Enterprise Compliance
When you move a snomed ct code lookup from a developer’s sandbox into a production environment, the entire game changes. Suddenly, speed, reliability, and security aren't just nice features to have—they're absolute necessities. Any application that touches sensitive patient data or drives a critical ETL pipeline lives and dies by its performance and compliance posture.
Trying to build this kind of enterprise-grade infrastructure from the ground up is a monumental task. It demands serious expertise in distributed systems, caching, and data security. This is exactly where a managed API solution becomes a lifesaver, handling the backend complexity so your team can focus on what they do best: building great applications, not babysitting vocabulary servers.
High-Performance Lookups at Scale
Nothing stalls a data pipeline faster than slow queries. To get those consistent, low-latency lookups, a modern vocabulary service has to lean heavily on intelligent caching and a global edge network. This architecture is designed to serve up frequently accessed concepts almost instantly—we're often talking response times under 50 milliseconds.
What makes this so effective is a fascinating pattern in clinical data. If you analyze real-world SNOMED CT usage, you’ll find that a tiny fraction of codes does all the heavy lifting. A mere 1,645 codes account for the top 99% of all usage, and the top 20 codes alone show up 11,148 times in analyzed datasets. This Pareto-like distribution is a massive advantage for biostatisticians and AI teams. With smart caching, these high-frequency codes are always hot and ready for immediate retrieval. You can actually explore these SNOMED CT code usage patterns and see this in action.
Meeting Enterprise Compliance and Security Standards
Performance is only half the battle, though. In healthcare, compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR isn't optional. It’s the cost of entry. Using a managed service that was built with these requirements in mind significantly de-risks your entire data operation.
Here are a few non-negotiable features you should be looking for:
- End-to-End Encryption: All data—in transit and at rest—must be encrypted. No exceptions.
- Immutable Audit Trails: You need a complete, unchangeable log of every single API call. This is crucial for security audits and compliance checks, where long-term retention of seven years or more is often the standard.
- Strict Access Controls: The ability to finely manage API keys and user permissions is essential to ensure only authorized people and applications can touch your vocabulary data.
Key Takeaway for Data Leaders: A managed API isn't just a technical shortcut; it's a strategic move. It lets you inherit a proven security and compliance framework that could otherwise take months or even years to build, validate, and maintain on your own.
By choosing a platform where these features are already baked in, you can meet enterprise security standards without pulling your engineers off mission-critical projects. If you need to dig into the technical details, the OMOPHub API documentation is the best place to start.
Common Questions About SNOMED CT APIs
When you're looking to use an API for a snomed ct code lookup, a few practical questions always come up. My team and I hear these all the time from developers and data scientists who are trying to figure out how this works in a real production environment. Let's walk through some of the most common ones.
A huge concern is always versioning. SNOMED CT is constantly being updated, and keeping a local vocabulary database current is a massive headache. This is where a managed API service really shines. It handles all the vocabulary versioning behind the scenes, automatically syncing with the latest OHDSI ATHENA releases.
What does that mean for you? It means your application is always querying the most up-to-date version of SNOMED CT without your team ever having to download, update, and validate the database. That entire tedious cycle just disappears.
Handling Different Concept Types
"Can the API find deprecated or non-standard concepts?" The short answer is yes, and this is a critical feature. You can easily query for both by filtering on the standard_concept flag in your API call. Standard concepts are the officially recognized, active terms you should be using in the OMOP CDM.
Non-standard concepts, on the other hand, include things like old, deprecated codes or various synonyms. The API maps these back to their current, standard equivalents. This is a lifesaver for ETL pipelines where you’re dealing with messy source data and need to map those legacy codes to the correct SNOMED CT concept to maintain data integrity.
Pro Tip: When you're cleaning up source data, a great workflow is to first look up a term and immediately check its
standard_conceptstatus. If it comes back as non-standard, you can just follow its relationship mapping to find the correct standard concept. This massively simplifies your mapping logic. For more details, see the API documentation.
Integrating into Production Pipelines
When it's time to move into a production environment, you'll want to use an official SDK. The OMOPHub SDKs for Python and R take care of the heavy lifting—things like API authentication, formatting requests, and parsing the responses. This cuts down on a ton of boilerplate code.
You can embed these SDK calls directly into your existing ETL scripts. Imagine it inside an Airflow DAG or a dbt model, programmatically enriching your data with standard concepts as it flows through the pipeline. That's how you do it at scale.
For more on making your implementation easy for your whole team to use, check out these API documentation best practices. And of course, for specific code examples and endpoint details, the official OMOPHub documentation is always the best source of truth.
Ready to stop wrestling with vocabulary databases and accelerate your development? With OMOPHub, you get instant REST API access to SNOMED CT and other essential vocabularies, backed by enterprise-grade performance and security. Sign up for free and make your first API call in minutes.


